Biocaxis > Products
> intermediates |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
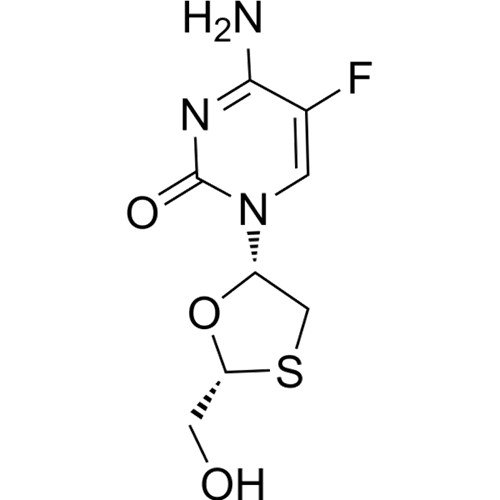 Emtricitabine
Emtricitabine
Catalog NO.: API-005 | CAS NO.: 143491-57-0 | Brand: BIOCAXIS
Category
Nucleosides & Nucleotides, API
Synonyms:
(-)-FTC; (-)-2′,3′-Dideoxy-5-fluoro-3′-thiacytidine,
(2R-cis)-4-Amino-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]-2(1H)-pyrimidinone,
4-Amino-5-fluoro-1-[(2R,5S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]-2(1H)-pyrimidinone,
5-Fluoro-1-(2R,5S)-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine, 524W91, BW
1592, BW 524W91, BW-1592, BW-524W91, BW1592, BW524W91, (−)-2′3′-Dideoxy-5-fluoro-3′-thiacytidine,
(2R,5S)-4-Amino-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]pyrimidin-2(1H)-one,
FTC
Emtricitabine is also known as FTC.
Molecular Formula
C8H10FN3O3S
Molecular Weight
247.25
General description
Emtricitabine is a synthetic nucleoside
analogue of cytidine, distinguished by its significant role in the field of
virological research, particularly targeting retroviruses such as HIV. Its
mechanism of action hinges on its ability to be incorporated into the viral DNA
by the reverse transcriptase enzyme, a critical player in the viral replication
process. Upon incorporation, emtricitabine acts as a chain terminator. It
effectively halts the elongation of the viral DNA chain, thereby obstructing
the virus′s ability to replicate. This unique action makes
emtricitabine useful in research aimed at understanding the dynamics of viral
replication and resistance mechanisms. It serves as a pivotal compound in the
study of viral lifecycle processes, offering insights that are for the development
of novel antiviral strategies and for enhancing our understanding of retroviral
behaviors at a molecular level. Through its study, researchers can probe the
intricacies of viral replication, resistance development, and the potential for
cross-resistance with other nucleoside analogues, contributing to a broader
comprehension of viral pathogenesis.
Emtricitabine ((-)-FTC) is an
orally active, non-cytotoxic (>100 μM/PBM, CEM, Vero, MT-4), potent
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) against HIV type 1/2 (HIV-1
IC50/culture = 8 nM/PBM (LAV-1), 9 nM/CEM (LAV-1); HIV-2 IC50/culture = 0.7
nM/PBM (ROD2), 100 nM/CEM (Zy)), hepatitis B, as well as simian and feline
immunodeficiency viruses. Emtricitabine is activated via 2′-deoxycytidine
kinase-mediated phosphorylation to (-)-FTC-5′-triphosphate that inhibits
viral reverse transcriptase in a dCTP-competitive manner (HIV-1 Ki = 2.9
μM).
Emtricitabine is an antiviral
drug that is used to treat chronic viral hepatitis, which is caused by the
hepatitis B and C viruses. The drug blocks the activity of reverse
transcriptase, which is an enzyme necessary for the replication of viral RNA in
the body. Emtricitabine has been shown to be effective against acute hepatitis
B virus infection and chronic hepatitis B virus infection with or without
cirrhosis. It also has been shown to be effective against chronic hepatitis C
virus infection with or without cirrhosis.

