Biocaxis > Products > Nucleotide |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
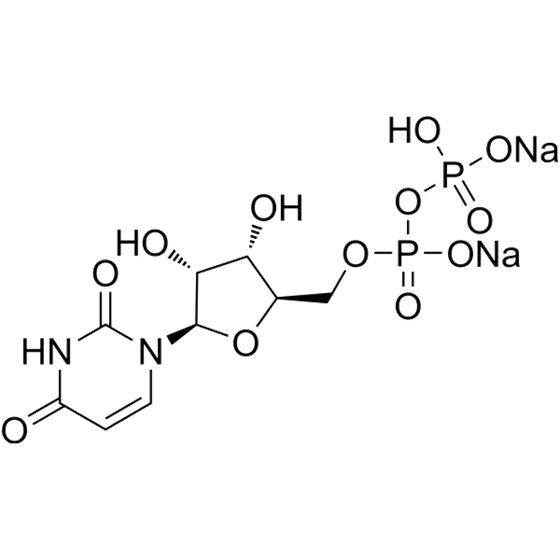 Uridine-5'-diphosphate disodium
Uridine-5'-diphosphate disodium
Catalog NO.: NDP-009 | CAS NO.: 27821-45-0 | Brand: BIOCAXIS
Category
Nucleosides & Nucleotides, Nucleotide
Synonyms
UDP disodium salt, Disodium 5′-UDP,
Disodium Uridine 5′-diphosphate, 5′-UDP-Na2
Molecular Formula
C9H12N2Na2O12P2
Molecular Weight
448.12
General description
Uridine-5'-diphosphate disodium salt is a potent, selective
P2Y6 receptor native agonist (EC50=300 nM; pEC50=6.52
for human P2Y6 receptor). Uridine-5'-diphosphate disodium salt, an endogenous
metabolite, catalyzes the glucuronidation of a wide array of substrates and is
used in nucleic acid (RNA) biosynthesis.
Uridine 5′-diphosphate
disodium salt hydrate has been used:
as a standard for quantification of metabolite levels in
murine tumor interstitial fluid by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
(LC/MS)
as a UDP standard for nucleotide analysis by liquid
chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS)
to treat E6.5 retina explants in vitro, to study its effect
on the entry and elongation of microglial cells into the embryonic quail retina
Biochem/physiol Actions
Uridine 5′-diphosphate (UDP)
is an endogenous signaling molecule produced by damaged cells to attract
macrophages. In response to neuronal damage, UDP promotes chemotaxis and chemokinesis in microglial cells.[3] UDP serves as a ligand
for P2Y receptors. UDP and uridine 5′-triphosphate
(UTP) may be used in studies on nucleic acid (RNA) biosynthesis and cell
signaling. UDP is a nucleotide that upon phosphorylation to UTP becomes a
substrate for enzymes such as RNA polymerase(s) and GTPases. These enzymes are
involved in a wide range of applications from the synthesis of RNA to the
regulation of G-coupled protein receptors (GPCR) and cell signaling molecules
such as Rho-signaling via guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF).

