Biocaxis > Products
> poly-nucleotide |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
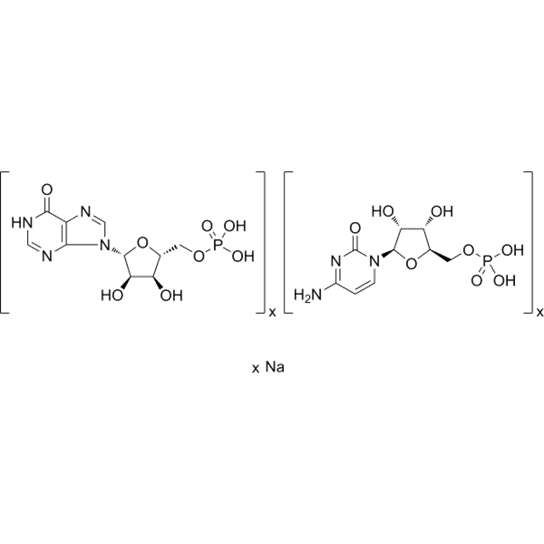 Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid sodium
Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid sodium
Catalog NO.: OLIG-006
| CAS NO.: 24939-03-5 | Brand: BIOCAXIS
Category
Nucleosides & Nucleotides, oligo
Synonyms:
Poly (I:C), Poly(I) • Poly(C)
Poly(I:C) sodium
Molecular Formula
(C10H13N4O8P)x.(C9H14N3O8P)x.xNa
Molecular Weight
General description
Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (Poly(I:C)) is a synthetic
analog of double-stranded RNA and an agonist of toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and
retinoic acid inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RIG-I and MDA5).
Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid can be used as a vaccine adjuvant to enhance
innate and adaptive immune responses, and to alter the tumor microenvironment.
Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid can directly trigger cancer cells to undergo
apoptosis.
Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium salt, often
referred to as poly(I:C), is a synthetic analog of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)
used extensively in molecular biology and immunology research. This compound is
recognized for its ability to mimic viral infection, which makes it useful for
studying the immune response to viral pathogens. Specifically, poly(I:C) is
utilized to activate toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), a component of the innate
immune system that detects dsRNA from replicating viruses. The activation of
TLR3 by poly(I:C) triggers downstream signaling cascades, leading to the
production of type I interferons and other cytokines. This response is central
to research on antiviral defense mechanisms and the development of vaccine
adjuvants. Additionally, poly(I:C) is used in studies focusing on the cellular
processes governing RNA interference, gene expression, and the role of dsRNA in
the regulation of these pathways. Its use as a model compound in the study of
dsRNA-protein interactions also contributes to the understanding of how cells
recognize and respond to viral infections at the molecular level.
TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA and is a major effector
of the immune response against viral pathogens. Polyinosinic–polycytidylic acid
(Poly(I) • Poly(C)) is a double-stranded homopolymer used as a model RNA to
study cell signaling at the level of TLR3. Poly(IC) is
a TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor-3 (TLR3) ligand.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Transfection of Poly (I:C) into NIT-1 cells has been used
as a model of intracellular dsRNA-induced β cell apoptosis. Eighteen hours
post transfection, 45% of the cells were apoptotic with an increase in NF-kB,
p50/p65 nuclear translocation, and cleavage of caspases 3 and 8, as well as
transcriptional induction of caspase 12, Fas, IL-15, and the TNF
receptor-associated ligand (TRAIL). It has been suggested that Poly(I:C) is one
of the most appropriate generators of stable mature dendritic cells (DC). These
mature DC might generate in vivo effective immune responses after injection due
to their ability to secrete bioactive IL-12 after CD40 ligation. Poly (I:C) was
used as a potent adjuvant to enhance the specific anti-tumor immune responses
against a peptide-based vaccine.

